As one of the most desirable financial market in the world, Hong Kong is especially preferred by business people. In Hong Kong, there are many entity types to adapt to different sizes and purposes of the enterprises. The business entities in Hong Kong can be classified into private and public company, limited by shares or guarantees, sole proprietorship, partnership, branch, and representative office.
Introduction
There are many business entity types in Hong Kong, and the ways of division are also various. This article is concentrating on the following kinds of firms in Hong Kong: Limited Liability Company, Sole Proprietorship, Partnership, Branch, and Representative Office.
1. Limited Liability Companies in Hong Kong
Main features of LLC
The Limited Liability Companies (LLC) in Hong Kong are categorized as private vs public companies and companies limited by shares vs limited by guarantees. The classification of these business entity types is based on the following features:
Private Limited by Shares
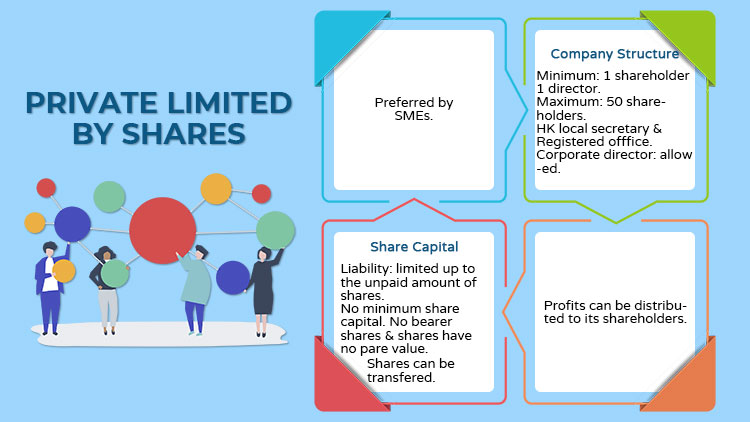
- Preferred by small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to conduct business and trade
- Company structure:
- Required at least one shareholder, one natural director, Hong Kong local secretary, and registered office
- Corporate director is allowed under strict circumstances
- Maximum of 50 shareholders
- Share capital:
- The liability of its members is limited up to the unpaid amount of shares held by each shareholder
- No requirement of minimum share capital
- No bearer shares & shares have no pare value
- Shares can be transferred but subject to the company’ refusal to register transfer of shares
- The company’s profits can be distributed to its shareholders
For a throughout look into this type of entity, read our blog Private Limited Company in Hong Kong!
Public Limited by Shares
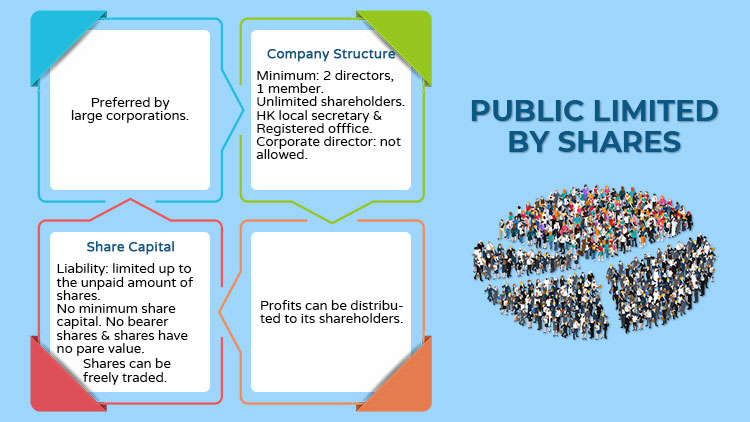
- Most chosen by large corporations to conduct business and trade
- Company structure:
- Required at least two directors, one member, Hong Kong local secretary, and registered office.
- Corporate directors are not allowed
- Can be more than 50 shareholders
- Share capital:
- The liability of its members is limited up to the unpaid amount of shares held by each shareholder
- No requirement of minimum share capital
- No bearer shares & shares have no pare value
- Shares can be freely traded.
- Shares of a public company may or may not be listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange.
- The company’s profits can be distributed to its shareholders
Company Limited by Guarantee

- Especially preferred by charities, societies, club, or non-profit organizations to raise funds for humanitarian purposes
- Company structure:
- Required at least two directors, one member, Hong Kong local secretary, and registered office.
- Corporate directors are not allowed
- Can be more than 50 shareholders
- Share capital:
- Company limited by guarantee does not have share capital
- The liability of its members is limited to an amount agreed to contribute in the event of the company’s liquidation
- The profits cannot be distributed among the members
Advantages of Private Companies
The on-going lines focus mostly on the Private Company Limited by Shares as it is a popular type for Hong Kong incorporation.
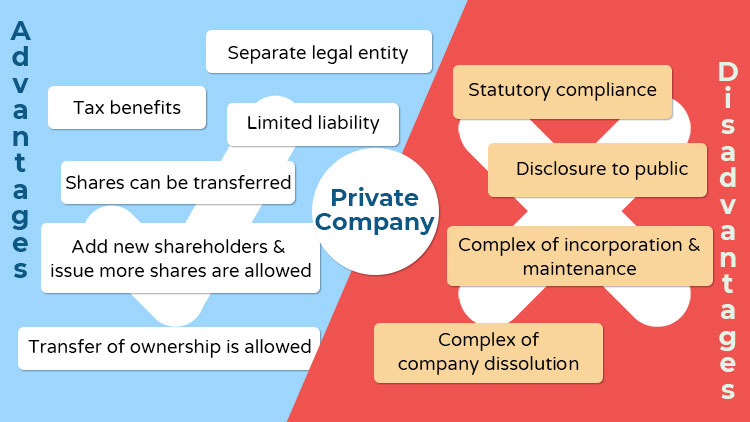
- Separate legal entity: A Hong Kong private company can acquire assets, go into debt, enter into contracts, sue, or be sued in its own name, due to the distinction from its founders. Its shareholders are not responsible for paying off its debts.
- Limited liability: The shareholders’ liability to the company is limited by their respective investment.
- Company life cycle: Shares can be transferred (according to the company’s AA), so the membership amendment does not affect the entity’s existence.
- Raising capital after incorporation: It is possible for private companies to bring new shareholders and issue more shares to expand its business.
- Transfer of ownership: Complete or partial transfer of ownership can be done by selling all or parts of its total shares or releasing new shares to the new investors.
- Tax benefits: Corporate tax regime in Hong Kong follows the territorial principles, which benefits its private companies with the tax rates from 8.25% to 16.5% for incomes derived from Hong Kong, and tax exemption for profits gained from the outside.
Free ebook
Everything you need to start doing business in Hong Kong
- Company registration process
- Compliance & tax requirements
- Employment & hiring issues

Disadvantages of Private Companies
- Statutory compliance: The Hong Kong private companies must do the compliance obligations annually with the Companies Registry and Inland Revenue Department, which increases the management workload.
- Disclosure to public: The identity of all shareholders and directors are required to publish according to Hong Kong Company Ordinance.
- Complex of incorporation and maintenance: It is more expensive for forming and maintaining a private company than a partnership or sole proprietorship.
- Complex of company dissolution: The closure of a private company is complicated, time-consuming, and costly compared to other entities.
Private companies are recommended if you are going to:
- Limit members’ liability in the business operation.
- Utilize the company to conduct the business as a separate legal body.
- Maximize finance support from the bank by using the movable assets of the company as security.
- Delegate your authority to other management personnel to conduct the business on your behalf.
2. Sole Proprietorship in Hong Kong
Main features of sole proprietorships
The sole proprietorship in Hong Kong is a basic business entity type. It is easy to register with the Business Registration Office. Operated by a single owner, this entity is connected fully with its sole investor. The business cessation causes upon the owner’s death. The company can be transferred only by selling business assets. There is no protection of personal assets from the liabilities, which makes it the riskiest company type.
The sole proprietorships in Hong Kong comply with the marginal tax rate from 7.5% to 15% depending on its income level. Unlike private entities, the reporting requirements are light as the owner is obliged to file only an annual tax return with IRD (form BIR60).
Advantages of sole proprietorships
- Easy registration and maintenance: Within one month after the business commencement, the owner must only apply for a Business Registration Certificate of the sole proprietor with Hong Kong Inland Revenue Department (IRD). Annual tax filing is required but audit task is exempted.
- Direct management: Decisions are made fast and easily as there is no need to discuss with other members.
- Gaining all profits: the proprietor is the sole beneficiary of all business profits, so he should have a good incentive to grow up the business.
Disadvantages of sole proprietorships
- Limited capacity to raise capital: The sole beneficiary’s personal wealth is the major source of capital; therefore, it might cause difficulty both at the beginning and the continuity stage of the proprietorship.
- No legal separation between personal and business assets: The company’s loss and debts are liable to the owner individually and unlimitedly. This person can be bankrupted by the court for being unable to pay off the debts.
- Heavy workload: The only founder of the sole proprietorship has the responsibility for decision making, problem-solving, operational duty, and business development. This is why the working pressure is higher than the other entity categories.
- Limited business life cycle.
Sole proprietorship is recommended if you are going to:
- Need an extremely simple registration and low cost of setting up & maintenance.
- Operate a limited and small scale of business scope.
- Have adequate funds to operate the business, without external financial support and expertise.
- Run low-risk (or non-risk) business.
3. Partnership in Hong Kong
Main features of partnerships
According to the Partnership Ordinance in Hong Kong, a partnership is formed when a person joins with other people to do business with a common view of intention for profits. This business entity type involves at least 2 members. There should be a partnership agreement, a mutual agreement among all the partners regulated by the Partnership Ordinance, to state and control their positions, rights, and obligations in the business. The firm must apply for a Business Registration Certificate no later than one month of business commencement. Hong Kong partnerships are in charge of the annual tax return by filing form BIR52 and subject to profits tax rate from 7.5% to 15%.
A partnership can be limited or general. Below is the comparison table for limited and general partnership.
| Limited partnership | General partnership |
|---|---|
|
|



