Tax evasion, Tax avoidance, and Tax planning are very common terms that you may have heard of before.
Understanding the differences between these terms is crucial for your business. It helps ensure that you’re not unknowingly committing an illegal act.
Let’s look at the facts related to the three principles and find out why they might or might not be a good idea for your business.
1. Tax planning for long-term benefits
Tax planning, like tax avoidance, is totally legal.
Generally, tax planning is the process of maximizing your tax benefits under eligible provisions of the tax framework. It reduces your tax liability through a variety of means, namely deductions, credits, rebates, and exemptions provided under the Income Tax Act or the corresponding tax laws.
To give an example, you can look for incentives from tax planning by saving via retirement plans. You can also make investments in fixed deposits, mutual funds, provident funds, or other similar accounts for the reduction of tax liability.
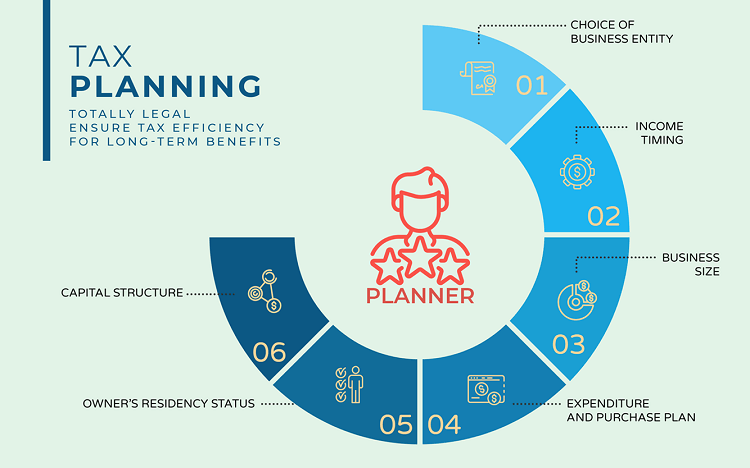
A key feature of tax planning is its relation to the future, whether short-term or long-term. To bring the best possible outcome for tax planning, you should take some essential factors into considerations:
- Choice of business entity
- Timing of income
- Size of business
- Planning for expenditures and purchases
- The owner’s residency status
- Capital structure
Among the three methods, tax planning is the most upright approach because it complies with the provisions of the tax laws. There are many strategies for good tax planning of your company, the key of which many startups and entrepreneurs have opted for incorporating an offshore company thanks to its great benefits of tax efficiency.
Tax havens, or “offshore financial centers” are efficient methods for tax planning purposes, offering an attractive tax regime and a high degree of secrecy for your business. Discover our latest findings on Hong Kong tax haven and its future prospects!
2. Tax avoidance is totally legal
You can get into a muddle over the meaning of tax evasion and tax avoidance. Those two terms may seem similar, but in fact, they are strikingly different. A highlight to note down is that tax avoidance is legal, whilst tax evasion is not.
Tax avoidance is the act of minimizing tax liability within the limits of the law or without breaking the law. In other words, you can use legitimate methods to reduce the amount of tax payable in association with your financial activities. The methods to avoid paying tax to the government may include the following:
- Using tax deductions for decreasing business expenses and business tax bill
- Delaying the payment of tax until a later date with an appropriate tax deferral plan
- Taking advantage of tax credits for legal purposes like business purchases, benefiting the company’s employees for sick leave and family leave
- Sheltering revenue from tax liability through the establishment of employee retirement plans.
It should also be noted that seeking reductions of tax obligations by tax avoidance is 100% legal, but it must be within four corners of the tax law framework. In some cases, it may lead you to step beyond the line to tax evasion, hence a violation of the jurisdiction regulations.
Thus, you should gain a good hold of relevant knowledge before using any tax strategies for minimizing taxes. In addition, you should engage financial experts for legal advice on how tax avoidance can be utilized most efficiently.
Learn more about how you can protect your income from taxes with our list of 5 Countries With No Income Tax That You Should Know!
3. Tax evasion is deemed as tax fraud

Tax evasion is an illegal method or unlawful attempt to reduce the tax liability of taxpayers. It refers to techniques or illicit practices of showing fewer profits to minimize the individual or company’s tax burden.
Examples of tax evasion usually are the following:
- Making false statements and information
- Inflating deductions without legal proof
- Hiding related documents to prove the earned business profits like records of transactions or reports of cash income
- Concealing or transferring assets illegally
- Magnifying tax credit
- Claiming excessive expenditure
Tax evasion is a form of tax fraud that indicates illegitimate and deliberate actions for not paying tax. Since employing such unfair means is fraudulent, any taxpayer regardless of individual or business committing tax evasion behaviors would be prosecuted for offense and must be subject to stringent punishments of a heavy fine or imprisonment.
4. Differences between tax evasion, tax avoidance, and tax planning
Businesses in search of saving tax often come up with those couple of terms. Each term has been clarified quite obviously in our above-mentioned sections. Below are key differences between tax evasion, tax avoidance, and tax planning to help you get a better understanding:
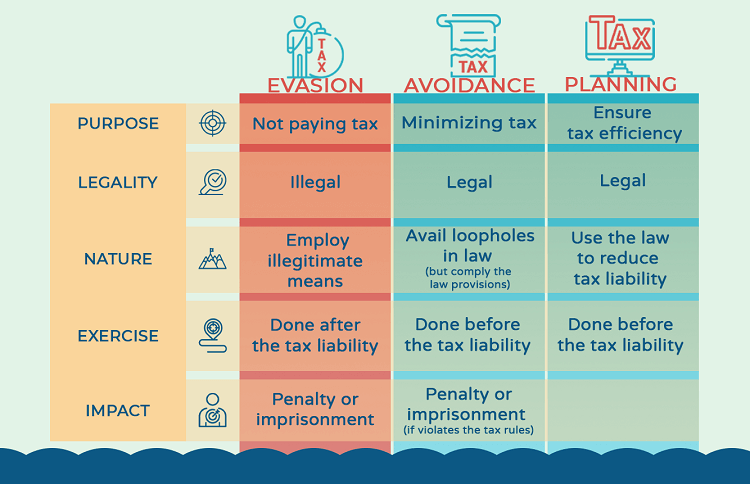
- Purpose: All serve for tax saving, but tax avoidance aims at minimizing tax, while tax evasion means not paying tax. Tax planning, on the other hand, helps businesses to ensure tax efficiency.
- Legality: Both tax planning and tax avoidance are legal. As considered as fraud, tax evasion is an illegal method to reduce tax.
- Nature: Tax avoidance is performed by availing loopholes in the law, but complying with law provisions. By contrast, tax evasion means employing illegitimate means for nonpayment of tax. Tax planning uses existing law provisions to relieve the burden of tax liability.
- How it is exercised: Tax avoidance is characterized as tax planning, but it is done before tax liability takes place. This method generally emerges in short-term benefits. Similar to tax avoidance, tax planning also should be done before tax liability arises, but it associates with the future and often serves for either long-term or short-term benefits of every assessee. Oppositely, tax evasion is typically done after the tax liability has arisen.
- Consequences: Tax avoidance is subject to penalty or imprisonment if it violates the tax regulations. Tax planning is legal, meanwhile, tax evasion must be subject to penalty and other kinds of punishment.
The taxes you pay will depend greatly on your business jurisdictions. You must understand the tax system of countries you’re operating in, to take advantage and maximize your tax benefits – take a look at our guideline of Hong Kong Tax System or Singapore Corporate Tax for more information!
5. Special considerations for choosing the right tax reduction manner
While the nature of tax planning is quite obvious, there seems to be some confusion over the difference between tax evasion and tax avoidance. As such, you should be fully aware of the tax practices being used.
In this regard, two essential tips that you need to take into account are as below:
- Acquire knowledge of tax laws and methods for the reduction of tax liability in the most efficient way. Keep in mind, differentiating such methods based on their purpose, legality, and features is very crucial as this would help you stay out of trouble and penalty.
- Seek advice from a professional tax expert or service firm. This is also a good idea as the person with his/her area of expertise will always know how to apply the tax law to decrease your tax burden and maximize your benefits. Furthermore, tax regulations are constantly changing, whether your tax-saving instrument is correct or not should be put under specific advice upon circumstances by tax experts as well.
In a nutshell, there are three instruments that taxpayers usually opt for minimizing their tax liability, including Tax planning, Tax avoidance, and Tax evasion. Each method provides a different manner for tax reduction. Note, however, that tax avoidance and tax planning are legal practices. By contrast, tax evasion is deemed as a means of fraud in most cases.
Feel free to get in touch with one of our friendly and experienced consultants for more practical advice!