Getting to know how the legal structures work, what impacts they have on business growth, and how to choose the right type of entity has always been challenging work since each business structure functions differently.
Whether you are just starting, or your business is growing, it is imperative that you understand all the options.
In today’s article, we look at the key factors to consider when choosing an entity structure in the US as well as the pros and cons associated, to help you decide which is best for your business.
Key elements to consider when choosing a business structure
First and foremost, you need to know about your options when it comes to selecting a business structure.
There are four main types of business structures that are widely used by entrepreneurs across the world, which are:
- Sole proprietorship
- Partnership
- Limited liability company (LLC)
- Corporation
With these four choices in mind, entrepreneurs will need to take into consideration the following factors when structuring a business.
Control and responsibility
Different entity types provide the owner with a certain level of control and responsibility. Being the only owner of a business will grant you more control than being the company’s partners, members, or shareholders.
However, with great control comes greater responsibility. For instance, if you’re the sole proprietor, you can control every aspect of the business, but you also have to carry all the work and responsibility.
Other forms of business, such as partnership, may offer less ownership, but in return, the responsibility can be divided and spread among several principals.
Extent of liability
When choosing business structures, also consider to what extent you would like to protect your assets and liabilities.
Some entity types provide limited liability protection, which helps safeguard owners’ assets in case the company goes bankrupt or suffers a loss.
In contrast, unlimited liability businesses mean the owners will hold complete responsibility for any debts or legal issues of the company.
Business owners should take into account this factor as it will affect their implications on potential liability.
Tax implications
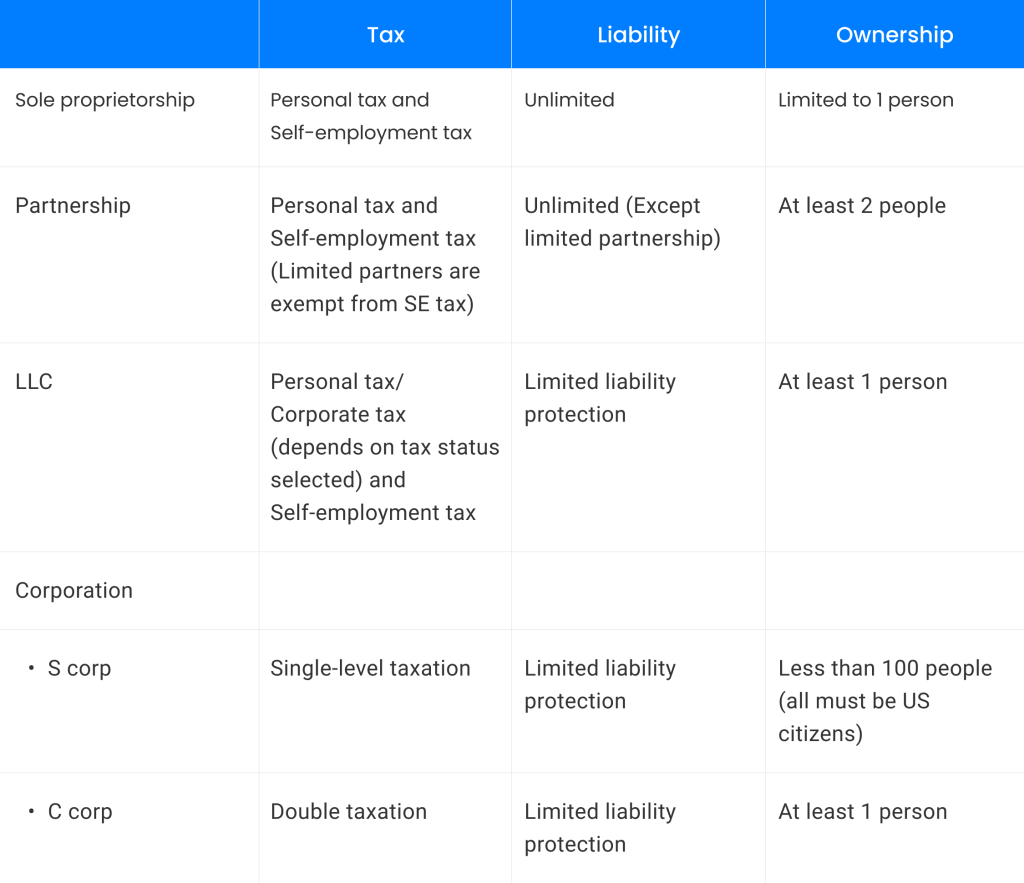
The type of structure you pick may determine business taxation and which taxes you must pay. The reason for this is that each business form is treated differently by tax authorities.
For instance, sole proprietors are normally taxed at the personal level because the owner and the business are considered the same legal entity.
For other entity structures such as an LLC or corporation, business owners will possibly pay corporate tax and personal tax, or additional specialty taxes imposed by the government.
Incorporation complexity
Each form of legal entity has distinctive setup procedures, costs and complexities involved. It is recommended for entrepreneurs to choose a business structure that can be set up easily or without any difficulty, involves reasonable expenses in formation, and has minimum legal formalities.
TIPS
Four main business structures in the United States: sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability company (LLC), and corporation, may come with their own advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to choose the right one for your business. If you need to seek quick and easy support for making decisions, you’ll want to give this US Business Entity Selection Tool a try.
Comparison of different US business entity structures
There are differences to each business structure, particularly when it comes to the advantages and disadvantages associated.
Here are some prominent pros and cons and the most common usage of 4 main entity types to help you decide:
Sole proprietorship
As its name would suggest, operating as a sole proprietor (or sole trader) means you are self-employed and running your small business by yourself. Some companies that began as sole proprietorships in the US and grew to multinational corporations include eBay, Walmart, JCPenney, Marriott Hotels.
Common uses of sole proprietorships
This form of entity is one of the most common legal structures for low-risk businesses and owners who want to test their business idea before officially running a more formal business.
It is also a widely preferred structure for rookie freelancers or self-employed individuals. For example, a freelance artist who sells his/her work on eCommerce websites or a personal trainer who offers one-on-one training for clients.
The advantages of sole proprietorships
- Complete control – Perhaps the biggest advantage of being a sole trader is the freedom to control the business and make any decisions as you please.
- Minimum administrative work – Setting up as a sole trader means you can avoid extra regulatory paperwork such as annual accounts, corporation tax returns, VAT returns, etc., and focus on planning your future and earning money.
- Low cost – The costs associated with incorporating and maintaining sole proprietorship may vary across countries but generally only include business license fees and taxes.
- Tax deduction – For sole proprietorship, the business and the owner are considered a single entity and thus, can be eligible for certain deduction claims, such as health insurance, wages, or premises.
The disadvantages of sole proprietorship
- Liability risks – In the eyes of the law, there is no difference between the sole traders and the business itself, which means the liability is unlimited and the owner will be personally liable for any business losses and debts.
- Difficulty obtaining financing – Getting finance to upscale businesses can be a challenge for sole traders as they can’t issue or sell stock. Moreover, lending institutions are less likely to give loans to sole traders because of limited assets and credibility.
Partnership
A partnership is where two (or more) people share the management and profits of a business. Partnerships can be created through formal agreements (e.g. written contracts, signed documents) or informal agreements (e.g. verbal contracts).
There are three main types of partnership and each has varying levels of liability and control.
- General partnership
- Limited partnership
- Limited liability partnership
Common uses of partnership
This type of entity is mostly popular for businesses with multiple owners or professional groups such as accountants, artists, or lawyers.
For instance, a musical artist can form a partnership with a PR specialist for promotion, or 2 lawyers partner up to launch a consulting firm.
There are many examples of successful partnerships in the United States. Some of the most notable include Warner Bros, Microsoft, Ben & Jerry’s, Apple, etc.
This blog Limited Liability Partnership: What Every Entrepreneur Needs to Know will tell you more interesting facts about this structure.
The advantages of partnerships
- Early-stage capital – Partnering with other members means your business has more chance to raise capital in the early stage. This can potentially increase the financial security and cash flow of your business.
- Ease of operation – Partners can share day-to-day tasks and major business decisions with each other (except for limited partnership), which helps boost business efficiency and productivity and lower the stress of operations.
- Tax treatment – Most partnerships are taxed as pass-through entities – each partner files and pay taxes on the share of ownership, reducing the burden of paying taxes on the entire business income.
- Knowledge and expertise – Operating with business partners mean you can benefit from various knowledge and expertise, especially if the partners specialize in areas where you are lacking. For rookie entrepreneurs, it is ideal to start a business with seasoned partners who can provide guidance and advice.
The disadvantages of partnerships
- Attorney costs – Although partnerships can be formed with informal arrangements, it is always best to sign a written agreement for protection. Coming to terms with ownership and responsibility may require an attorney to review, which takes more time and money to settle.
- Partner’s liability – Being in a partnership means you can be personally responsible for any fault actions or mistakes your partner makes. In addition, your assets have the possibility of being used to cover the partnership’s debt. To protect your best interests, it is recommended to enter a potential partnership with someone you trust.
- Conflict among partners – With multiple partners, there are bound to be disputes and conflicts. Any disagreement between partners can cause the dissolution of the partnership, especially in cases of partnerships among family members or close friends, where personal judgment can affect professional issues.
Limited liability company (LLC)
A limited liability company, better known as LLC, is considered one of the most common entity structures.
Google chose an LLC as the business structure for their company when they started out. Other well-known companies that have chosen LLCs as their business structure include: Pepsi-Cola, Johnson and Johnson, Sony, eBay, IBM, Nike, Airbnb, etc.
The flexible nature of LLCs made it the ideal choice for a startup that was still figuring out its business model. These companies all had one thing in common when they started out: they were all startups with innovative business models that were still being tested and perfected. LLCs allowed them the flexibility to experiment with their business models without incurring too much risk.
Now that these companies have become established, they have switched to different business structures: C corporation, Public Benefit Corporations (PBCs), Limited Liability Partnerships and so on.
Unlike sole traders or partnerships, an LLC is a separate and distinct legal entity, which provides protection and limited liability to its owners.
Common uses of LLCs
LLCs are commonly used among small or medium-scale businesses, where the owners have substantial amounts of personal assets they want to protect.
On the same note, if you are operating in an industry with a high risk of civil lawsuits such as manufacturing, construction, or healthcare, having an LLC as your legal structure can potentially protect you from any potential loss or liability.
The advantages of limited liability companies
- Limited personal liability – The name of this structure tells how ownership is held liable. The liability of an LLC owner is limited, meaning that in the case of a business loss, personal assets such as your house, vehicle, and savings accounts, are protected from liability. This helps business owners control their exposure to financial risk.
- Improved credibility – An LLC is deemed a formal business structure (along with corporations), eventually boosting reputation and prestige. Clients and brands in the financial sector especially prefer to work with LLCs. This may potentially lead to new business opportunities and profitable contracts.
- Favorable tax regime – An LLC enjoys substantial tax benefits with a considerably lower rate compared to other entity structures, offering greater flexibility for tax planning.
The disadvantages of limited liability companies
- Maintenance and paperwork – Generally, LLCs are required to file annual reports with governance authorities to keep good standing, which increases the burden of paperwork for business owners. The reporting requirements normally include statements, records, and meticulous document and filing processes.
- Costs for renewal – In many jurisdictions, LLCs must renew their licenses yearly. The fees for LLCs renewal are typically higher compared to other entity forms.
- Limited investment options – Although LLCs can acquire investment through equity financing, debt financing, or crowdfunding, they cannot issue shares to outside investors; thus, limiting the options available.
Related reading: Detailed explanations about Pros and Cons of Choosing LLC in the USA
Although investors can still make a financial contribution by becoming a member or co-owner of the LLC, this may potentially disrupt the structure of the business and affect the decision-making process.
Corporation
A corporation is a legal entity that is completely independent and separate from its owners. There are many different types of corporations in the United States, each with its own unique benefits and drawbacks. The most popular types are C-corps (double taxed) and S-corps (not double taxed).
There are also several types of corporations:
B corporations are for-profit companies that are certified by the nonprofit B Lab to meet rigorous standards of social and environmental performance, accountability, and transparency. To simply explain, B corps use the power of business to solve social and environmental problems.
Close corporation is a type of business entity that is designed for businesses with a small number of owners. In spite of its flexibility in management and decision-making, as well as reduced paperwork and compliance requirements, close corporations typically have limited life spans and cannot go public or raise capital through the sale of stock.
Nonprofit corporations are formed for religious, charitable, scientific, literary, or educational purposes. These organizations can apply for 501(c)(3) status from the IRS, which exempts them from paying federal corporate income taxes on money earned from activities related to their mission.
Examples of Corporations in the US include Amazon, JPMorgan Chase, General Motors,Exxon Mobil Corp, etc.
Common uses of corporations
This business structure is popular for businesses that have lots of growth potential that wish to attract large amounts of capital and scale quickly in the future.
Corporations also make sense for businesses with many outside investors because they offer the benefit of raising capital by selling stock.
Furthermore, corporations can be used for not-for-profit purposes which are dedicated to a specific social cause such as educational, religious, scientific, or research.
The advantages of corporations
- Limited liability – Stockholders are not personally liable for claims against the corporation; they are only responsible for their personal investments.
- Secured business finance – As a formal entity structure, corporations are more likely to be considered for investment and capital injection by lending institutions. Furthermore, a corporation can raise capital by issuing new shares to the public and new investors, which presents a substantial opportunity to secure business finance and fundraising.
- Business continuity – Unlike other entity forms, corporations are not affected by the transfer of ownership. The business continues to operate in the long term, which is preferred by investors, creditors, and consumers.
The disadvantages of corporations
- Double taxation – Corporations like C-corps face double taxation, meaning the business income is taxed at both entity and personal levels (based on the percentage of profits earned). This can, in some cases, be avoided by filing as an S corporation.
- Extensive obligations – Running a corporation comes with a large number of formalities and responsibilities. Apart from upfront filing, other duties include filing annual reports, following strict record-keeping procedures, conducting annual general meetings, and maintaining details of shareholders, directors, officers, and employees.
- Expensive to set up – Forming and maintaining a corporation tend to be costly due to large amounts of initial capital as well as filing charges, ongoing fees, and taxes.
Conclusion
At this point, you have obtained specific knowledge about different entity types and how to choose a legal structure for your business.
In the end, there is no one-size-fits-all type of entity structure. Each structure has distinct characteristics and knowing how to utilize these features is the first step to becoming a successful business. If you are a foreigner looking to register a US company, there are a few key steps that you need to take in order to ensure the process goes smoothly. Check out a brief overview of what you need to do right away:
Steps to register a US company for non-residents
If this article has piqued your interest somewhat, and you want to start your business structure of choice, you can wrap up the entire process online with our company formation service, we can take care of it on your behalf!
Disclaimer: While BBCIncorp strives to make the information on this website as timely and accurate as possible, the information itself is for reference purposes only. You should not substitute the information provided in this article for competent legal advice. Feel free to contact BBCIncorp’s customer services for advice on your specific cases.
Get helpful tips and info from our newsletter!
Stay in the know and be empowered with our strategic how-tos, resources, and guidelines.



